Prose and verse are two fundamental forms of written expression in literature. While prose is used for everyday communication and storytelling, verse is structured and often used in poetry and lyrical compositions. Understanding their differences is crucial for literary analysis, creative writing, and appreciation of language. This article explores their characteristics, differences, examples, and significance in literature.
What is prose and verse?
Prose is a form of written or spoken language that follows natural speech patterns without a structured meter or rhyme. It is the most common way of writing in everyday communication, storytelling, essays, articles, novels, and speeches. Unlike poetry, which often has a rhythmic or musical quality, prose focuses on clear expression, logical flow, and grammatical structure.
Types of Prose
Prose can be categorized into different types based on its purpose, style, and structure. Here are the main types:
-
Narrative Prose – Tells a story with characters, plot, and setting.
-
Examples: Novels, short stories, fairy tales, fables.
-
Example: The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
-
Descriptive Prose – Focuses on vivid imagery and sensory details.
-
Examples: Travel writing, nature writing, character descriptions.
-
Example: A travelogue describing the landscapes of Iceland.
-
Expository Prose – Presents facts, explains ideas, or provides information.
-
Examples: Essays, textbooks, and news articles.
-
Example: A science textbook explaining photosynthesis.
-
Persuasive Prose – Aims to convince the reader of a viewpoint or argument.
-
Examples: Editorials, speeches, and advertisements.
-
Example: Martin Luther King Jr.’s I Have a Dream speech.
-
Dialogue Prose – Written conversation between characters.
-
Examples: Scripts, plays, interviews.
-
Example: A screenplay for a movie.
-
Prose Poetry – Blends poetic elements with prose structure.
Also, read How to write an Evaluation Essay
A verse is a form of writing that follows a rhythmic structure, often with a specific meter and sometimes a rhyme scheme. It is commonly used in poetry, songs, and plays to create a musical or artistic effect. Unlike prose, which follows natural speech patterns, verse is more structured and can be formal or free-flowing, depending on the style.
Types of Verse
-
Rhymed Verse – Contains a consistent rhyme scheme (e.g., sonnets).
-
Blank Verse – Unrhymed but follows a specific meter, like iambic pentameter (e.g., Shakespeare’s plays).
-
Free Verse – No set rhyme or meter, but still poetic in form (e.g., modern poetry).
Examples of Verse
-
Poetry: “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe.
-
Song Lyrics: Many songs are written in verse form.
-
Plays: Shakespeare’s Hamlet contains large sections of verse.
Characteristics of Prose
1. Lack of Formal Structure
Prose does not adhere to specific meter, rhyme, or line break rules. It flows naturally like spoken language and is structured into sentences and paragraphs. This lack of constraint allows for narration, argumentation, and exposition flexibility.
2. Natural Flow of Language
Prose reflects the patterns of everyday speech, making it accessible and relatable. It focuses on clarity and coherence, using grammatical rules to convey ideas effectively.
3. Common Uses
Prose is used in various forms of writing, including:
- Novels & Short Stories – Fictional narratives that develop characters, plots, and themes.
- Essays & Articles – Informative and analytical compositions presenting arguments and viewpoints.
- Speeches & Presentations – Spoken communication that conveys ideas clearly and persuasively.
4. Does not rely on rhyme or musicality
Characteristics of Verse
1. Structured Form
Unlike prose, verse follows a specific structure, often divided into lines and stanzas. It utilizes rhythm, meter, and sometimes rhyme to create musicality and artistic effect.
2. Use of Meter and Rhyme
Verse often employs metrical patterns that establish rhythm. Common meters include:
- Iambic Pentameter – Five pairs of unstressed and stressed syllables (e.g., Shakespearean sonnets).
- Dactylic Hexameter – Six feet per line, commonly used in epic poetry (e.g., Homer’s works). Rhyme schemes, such as AABB or ABAB, add musicality and enhance memorability.
3. Common Uses
- Poetry – Aesthetic and emotional expressions through structured language.
- Songs & Lyrics – Musical compositions that rely on rhythm and poetic techniques.
- Dramatic Works – Classical plays (e.g., Shakespeare) often mix prose and verse.
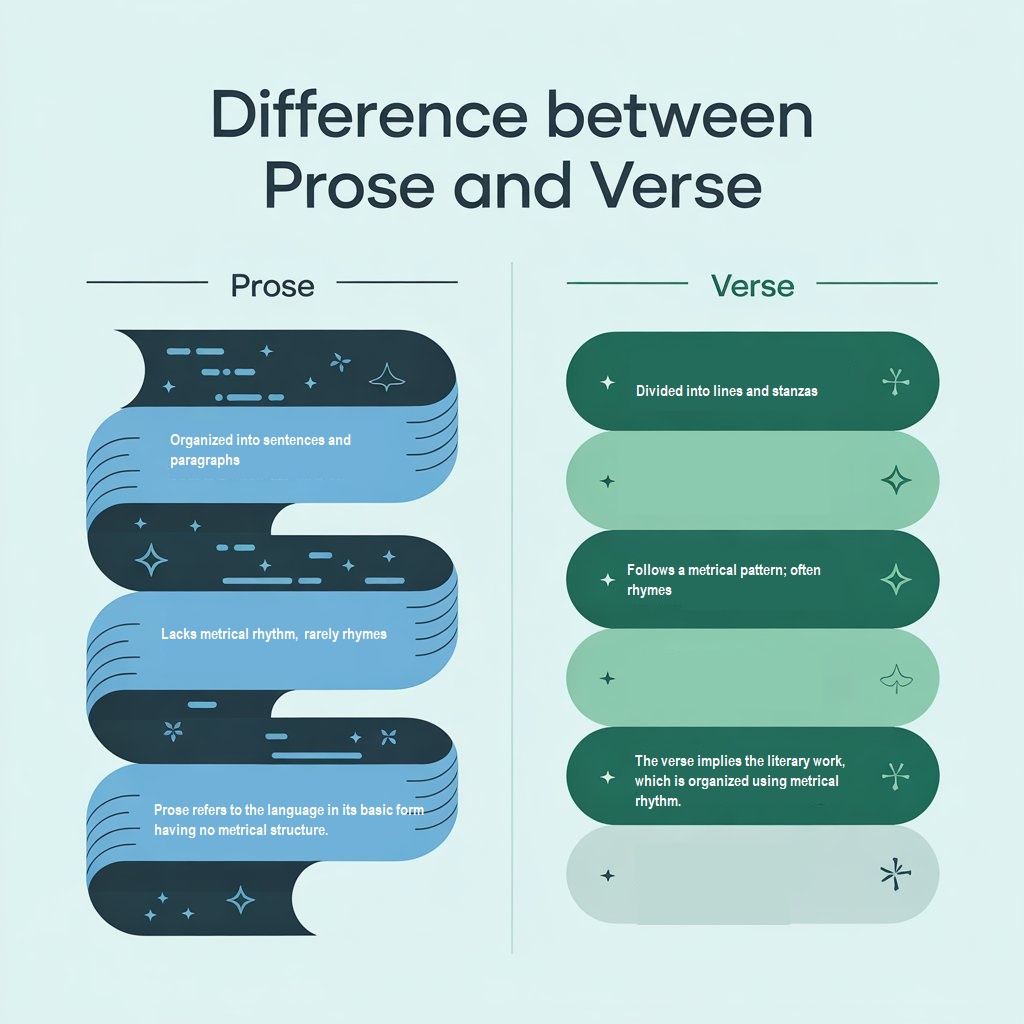
Differences Between Prose and Verse
|
Prose |
Verse |
| Structure |
Organized into sentences and paragraphs |
Divided into lines and stanzas |
| Rhythm & Rhyme |
Lacks metrical rhythm; rarely rhymes |
Follows a metrical pattern; often rhymes |
| Language Style |
Natural, everyday speech |
Poetic, often figurative and stylized |
| Purpose |
Communicates ideas clearly; tells stories |
Evokes emotions; explores deeper themes |
| Usage |
Novels, essays, speeches, articles |
Poetry, songs, plays |
Examples of Prose and Verse
Prose Examples:
- Novel Excerpt: “The sun was setting, casting a warm orange glow across the horizon. Sarah walked along the sandy beach, feeling the gentle breeze on her skin.”
- Speech Excerpt: “In his address, the professor presented a compelling argument supported by extensive research and data.”
Verse Examples
- Poem Excerpt: “Under the golden sun’s embrace,
A field of flowers sways with grace.”
- Song Lyrics: “In the depths of night, the stars ignite,
Twinkling diamonds in the celestial height.”
Significance of Understanding Prose and Verse
1. Enhances Literary Appreciation
Recognizing the structural and stylistic differences helps readers analyze texts more deeply, appreciating the artistry in writing.
2. Improves Writing Skills
Understanding prose and verse enhances creative and academic writing, allowing writers to choose the best format for their message.
3. Expands Communication Skills
Knowing when to use prose for clarity and verse for artistic effect improves written and spoken communication.
Prose and Verse: Their Significance in Literature
In literature, prose and verse serve distinct purposes, each contributing uniquely to storytelling, expression, and artistic impact.
Significance of Prose in Literature
-
Clarity and Accessibility – Prose allows for precise and direct communication, making complex ideas easier to understand.
-
Realism – Used in novels and stories, prose reflects everyday speech and thought patterns, making narratives relatable.
-
Narrative Depth – Prose provides the flexibility to develop intricate characters, settings, and plots.
-
Versatility – It is used across various genres, including fiction, nonfiction, and academic writing.
-
Descriptive Power – Allows detailed imagery and explanation without constraints of meter or rhyme.
Significance of Verse in Literature
-
Musicality and Aesthetic Appeal – The rhythmic quality of verse makes it pleasing to read and hear.
-
Emotional and Expressive Depth—The verse structure powerfully conveys emotions through poetic devices like metaphor, alliteration, and symbolism.
-
Memorability – The rhythm of the verse makes it easier to remember, which is why it’s often used in oral traditions and epic poetry.
-
Dramatic Effect – In plays, particularly in Shakespearean drama, verse heightens dramatic tension and distinguishes characters’ speech.
-
Cultural and Artistic Value – Verse has historical significance in storytelling, religious texts, and artistic expression across cultures.
Prose vs. Verse in Literature
-
Prose is often used in novels and short stories for detailed, realistic storytelling.
-
The verse is familiar in poetry and drama to evoke emotions, create rhythm, and add artistic beauty.
-
Some literary works blend both, such as Shakespearean plays, which mix prose (for commoners) and verse (for noble characters).
FAQ
Q1: Is prose always written in paragraphs?
Yes, prose is typically written in paragraphs, organizing ideas clearly and logically.
Q2: Can verse be used in prose writing?
Yes, verse elements (such as rhythm or poetic language) can be incorporated into prose, especially in poetic prose or lyrical narratives.
Q3: Can prose and verse be mixed?
Many works (e.g., Shakespeare’s plays) blend prose and verse to enhance storytelling and dialogue.
Q4: Are there exceptions to the characteristics of prose and verse?
Some experimental or hybrid literary works challenge traditional distinctions, blending prose and verse uniquely.
Conclusion
Both prose and verse play vital roles in literature, offering distinct ways to express ideas, emotions, and narratives. Prose provides clarity and depth in storytelling, while verse adds rhythm and artistic beauty. Understanding their differences enriches one’s appreciation of literature and enhances writing skills. Whether reading a novel, poem, or speech, recognizing the power of prose and verse allows for a deeper engagement with language and meaning.









 Evan John
Evan John