Cell biology illustrated report
Cell biology is the branch of science that studies cells and their characteristics. Cells are the fundamental units of life and provide a basis for understanding the structure and function of living organisms. By exploring the intricate processes occurring within cells, scientists can unravel the mysteries of life itself. We will look at Cell biology illustrated report.
Check also on Biology Assignment Help
Cell Structure
Cells possess a complex structure consisting of various components that work together to maintain their integrity and carry out vital functions. Let’s examine the key elements of a cell.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, forms a barrier between the cell’s internal environment and the external surroundings. It regulates the entry and exit of substances, ensuring a controlled exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm fills the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It houses various organelles and serves as a medium for biochemical reactions, facilitating cellular processes.
Nucleus
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material, DNA. It regulates cellular activities and contains the instructions necessary for cell growth, reproduction, and function.
Organelles
Organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions. These include mitochondria, responsible for energy production, endoplasmic reticulum, involved in protein synthesis, and Golgi apparatus, which modifies and packages proteins.
Cell Division
Cell division is a crucial process that ensures the growth, development, and regeneration of living organisms. There are two primary types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis
Mitosis is the division of somatic cells, resulting in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells. It plays a vital role in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction.
Meiosis
Meiosis occurs in specialized cells called gametes, which are involved in sexual reproduction. It involves two rounds of division and results in the formation of four genetically diverse daughter cells.
Read also on Lab report writing help
Cellular Processes
Cells engage in a range of processes that are essential for their survival and function. Let’s explore some of these fundamental cellular processes.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which cells produce an identical copy of their DNA. It ensures the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Transcription and Translation
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template, while translation is the process of converting RNA into proteins. These processes are vital for protein synthesis and gene expression.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis involves the assembly of amino acids into complex proteins. Proteins play a crucial role in various cellular functions, such as enzyme activity, cell signaling, and structural support.
Cell Signaling
Cell signaling allows cells to communicate and coordinate their activities. It involves the transmission of signals through molecular messengers, enabling cells to respond to changes in their environment.
Cell Metabolism
Cell metabolism refers to the chemical reactions that occur within cells to sustain life. Let’s explore some key aspects of cellular metabolism.
Energy Production
Cells require energy to carry out their functions. Through various metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, cells generate energy-rich molecules like ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert organic molecules, such as glucose, into ATP. It occurs in multiple stages, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process exclusive to plants, algae, and some bacteria. It involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, resulting in the production of glucose and oxygen.
Cell Differentiation and Specialization
During development, cells undergo differentiation, a process where they become specialized for specific functions. This specialization enables cells to form different tissues and organs, contributing to the complexity of multicellular organisms.
Cell Cycle Regulation
The cell cycle refers to the series of events that a cell undergoes from its formation to its division. Regulation of the cell cycle ensures proper growth, repair, and reproduction, preventing abnormalities like cancer.
Importance of Cell Biology
Cell biology is of paramount importance as it provides the foundation for understanding life at its core. By studying cells, scientists can gain insights into diseases, develop new treatments, and advance our knowledge of the natural world.
Related article Biotechnology Assignment help
Cell biology illustrated report Sample Questions
I need to write a 4000 word cell biology illustrated report using Harvard method. Below are questions
Unit Introduction
1.1: Discuss selected characteristics of living cells
1.2: Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and also the impact viruses have on them
1.3: Discuss eukaryotic sub-cellular structure and organelles
2.1: Explain the role of the cell membrane in regulating nutrients and waste products in illustrated cell biology
2.2: Explain how animal cells use nutrients to provide energy for growth, movement and cell division in particular
2.3: Discuss the synthesis of proteins
2.4: Explain the role of nucleic acids in the nucleus and cytoplasm
3.1: Explain the generation of specialised tissues from embryonic stem cells
3.2: Explain the importance of interphase and factors that initiate cell division
3.3: Explain how the same genetic information is received by each daughter cell
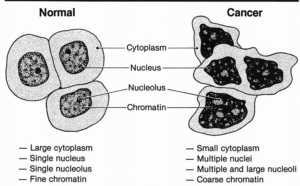
3.4: Compare and contrast cancer cells with normal cells
In case you may need to read more on article in biology. At elite academic brokers we provide excellent biology assignment help. We have various experts in biology who give high quality output in biology.
Why You Should Choose Elite Academic Brokers’ Unique Services
Our services are unique and we offer the best biology solution.
- Our biology experts ensure they read and understand all the guidelines, as well as, all instructions given in the rubric before starting a cohesion writing.
- They do extensive research for the biology homework from credible sources such as books, journals, articles, and others.
- Our biology experts are well conversant with all referencing styles such as MLA, IEEE, APA, and others.
- All our tasks are free from plagiarism as we check for similarity and plagiarism using a Turnitin.
- All our tasks are cheap and affordable which does not compromise the quality of work.
- Our payment methods are safe and secure and the client is at liberty to choose the payment method that is convenient to them.
- We also do the most urgent orders and these tasks take the shortest time possible, for instance.
At Elite academic brokers we offer various services like lab report and many others.
FAQ
1. What is Cell Biology?
Cell biology is the branch of science that focuses on the study of cells, their structure, function, and the processes that occur within them. It encompasses various aspects of cellular life, including cell division, metabolism, communication, and differentiation. Cell biology provides a foundation for understanding the complexity of living organisms, as cells are the basic building blocks of life.
Three important pieces of information about Cell Biology:
Cell biology is the study of cells and their functions.
It involves the investigation of cellular processes such as cell division and metabolism.
Cells are the fundamental units of life and are responsible for the structure and function of organisms.
2. What are the main components of a cell?
Cells consist of several key components that work together to carry out various functions. The main components of a cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, and genetic material.
Three important pieces of information about the main components of a cell:
The cell membrane acts as a barrier, separating the internal environment of the cell from the external environment.
The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and houses various organelles.
Organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions, such as mitochondria for energy production and the nucleus for storing genetic material.
3. How do cells reproduce?
Cells reproduce through a process called cell division, which involves the replication and distribution of genetic material. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Three important pieces of information about cell reproduction:
Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs in most cells, where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in cells involved in sexual reproduction, resulting in the formation of gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the number of chromosomes.
Cell division is essential for growth, repair, and the production of new cells in multicellular organisms.
4. What is the role of DNA in cells?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic information of an organism. It plays a crucial role in cells by encoding the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and controlling various cellular processes.
Three important pieces of information about the role of DNA in cells:
DNA contains the genetic code that determines the characteristics and functions of an organism.
The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins that carry out specific functions in the cell.
DNA replication ensures that the genetic information is faithfully passed on to daughter cells during cell division.
5. How do cells communicate with each other?
Cellular communication is vital for coordinating various processes within multicellular organisms. Cells communicate through direct contact, chemical signals, and electrical signals.
Three important pieces of information about cellular communication:
Direct contact between cells allows for the transfer of signals and molecules through gap junctions or cell surface receptors.
Chemical signals, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, are released by cells and travel through the bloodstream or extracellular fluid to target cells, initiating specific responses.
Electrical signals, such as action potentials in nerve cells, allow for rapid communication over long distances









