As a student, it’s crucial to understand the differences between abstract vs conclusion. An abstract gives a quick overview of the whole paper, thus encouraging readers to read through it. A conclusion ties everything together, emphasizing the study’s significance. If the student understands these distinctions it will help them write research papers very clearly and effectively, ensuring they pass very well in their end-of-term assignment. At the end of the semester students in one way or another will be required to write a research paper or term paper. Making this very important for students
What is an abstract for a research paper?
What is the conclusion of the research paper?
In a research paper, the conclusion serves as the final section where you wrap up your study and provide a summary of your findings. It’s an opportunity to reiterate the main points of your research and to highlight the significance of your findings in the context of your research question or hypothesis. Additionally, the conclusion often includes reflections on the implications of your research, suggestions for future research directions, and perhaps even practical applications of your findings. Ultimately, the conclusion should leave readers with a clear understanding of the contributions your study has made to the field and the broader implications of your work.
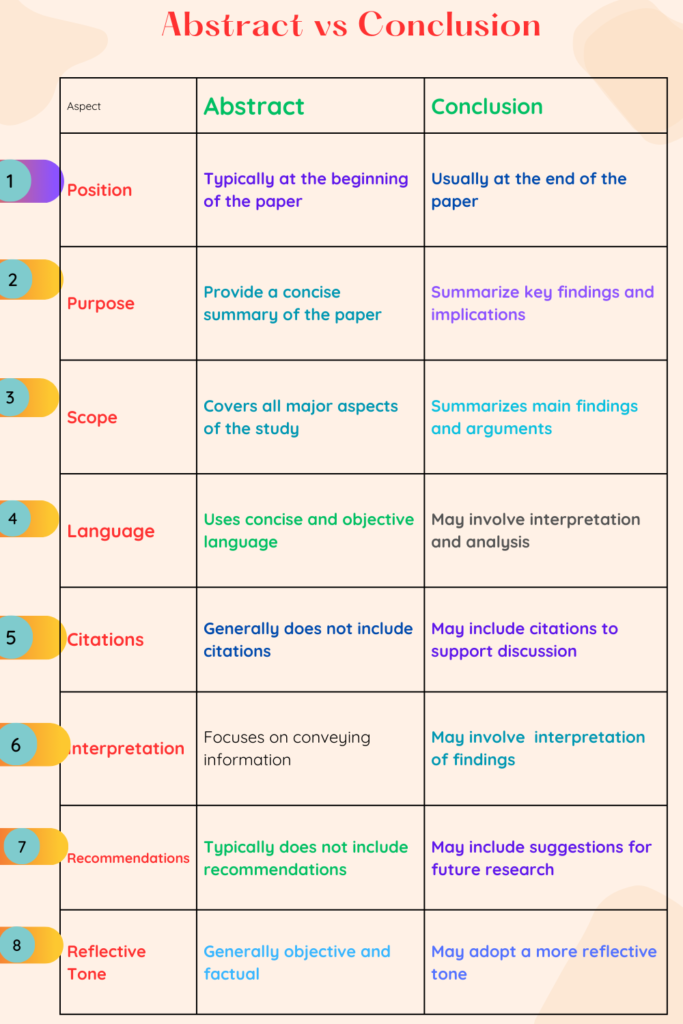
Difference between Abstract vs Conclusion in a research paper
Abstract
- Position: The abstract is usually placed at the beginning of a research paper, before the main body of the text.
- Purpose: Its primary purpose is to provide a concise summary of the entire research paper, including its objectives, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Length: Typically, abstracts are relatively short, ranging from 150 to 300 words, depending on the requirements of the journal or conference.
- Content: An abstract gives readers a quick overview of the study without delving into detailed discussions. It highlights the key points and findings of the research.
- Audience: Abstracts are aimed at a broad audience, including researchers, scholars, and professionals in the field, as well as those seeking a general understanding of the topic.
- Scope: Abstracts provide an overview of the entire paper, covering all major aspects such as the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. They encapsulate the essence of the study succinctly.
- Language: Abstracts use concise and objective language, focusing on conveying information rather than providing interpretations or reflections. They avoid personal opinions or subjective evaluations of the research.
- Citations: Abstracts typically do not include citations or references to other works. Instead, they focus solely on summarizing the content of the research paper itself.
Read on Abstract of a Research Paper
Conclusion
- Position: The conclusion is located at the end of the research paper, following the main body and any discussion or analysis sections.
- Purpose: Its main purpose is to summarize the main findings and insights of the study, reiterating the significance of the research and its implications.
- Length: While the length can vary depending on the length of the paper and the depth of the discussion, conclusions are typically longer than abstracts, spanning a few paragraphs to a page.
- Content: In the conclusion, researchers often reflect on the research process, discuss the implications of their findings, and suggest avenues for future research. It provides closure to the paper by tying together all the elements discussed in the study.
- Audience: Conclusions are primarily targeted at readers who have already engaged with the entire paper and are seeking a deeper understanding of the study’s significance and broader implications.
- Scope: Abstracts provide an overview of the entire paper, covering all major aspects such as the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. They encapsulate the essence of the study in a succinct manner.
- Language: Abstracts use concise and objective language, focusing on conveying information rather than providing interpretations or reflections. They avoid personal opinions or subjective evaluations of the research.
- Citations: Abstracts typically do not include citations or references to other works. Instead, they focus solely on summarizing the content of the research paper itself.
Final Thought









 Evan John
Evan John